

You can compare the current file with a hash value in the clipboard by using the Hash Comparison box or use the “Compare a file” button to compare another file with the selected one. These include the Keccak, RIPEMD, SHA and MD families along with several others like GOST, ED2K, Adler32, and Tiger. Pressing Settings gives access to an impressive selection of 27 additional hash values that can all be displayed. One major limitation HashTab has compared to HashCheck is it only works on one file at a time. After right clicking on the file and going to Properties, the tab is called “File Hashes” and you will get CRC32, MD5 and SHA-1 hash values displayed by default. HashTab is another tool that uses the system file properties window to show file hashes and is quite similar to HashCheck. The 7z.exe command line tool has this function by using the “h” command along with a hash switch “-scrc.
Do note that when you select multiple files 7-Zip will give the overall checksums for all files added together and not each file individually. Just right click on a file and go to “CRC SHA” and the options will be available to get a checksum for CRC-32, CRC-64, SHA1, SHA256, or the asterisk will get all at once (including BLAKE2sp).
A few years later a function was added to 7-Zip that introduced a context menu entry where you can quickly check a file’s integrity through the program’s user interface. The ability to verify file checksums with CRC or SHA has been in 7-Zip since 2011.
#DUPLICACY HASH COMMANDLINE ARCHIVE#
Not least because of its 7z archive format that can achieve great compression ratios.
#DUPLICACY HASH COMMANDLINE FREE#
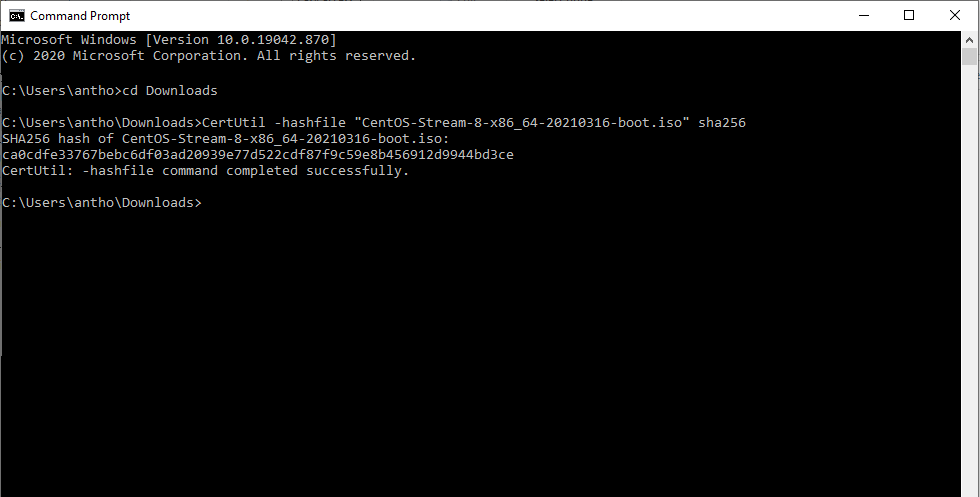
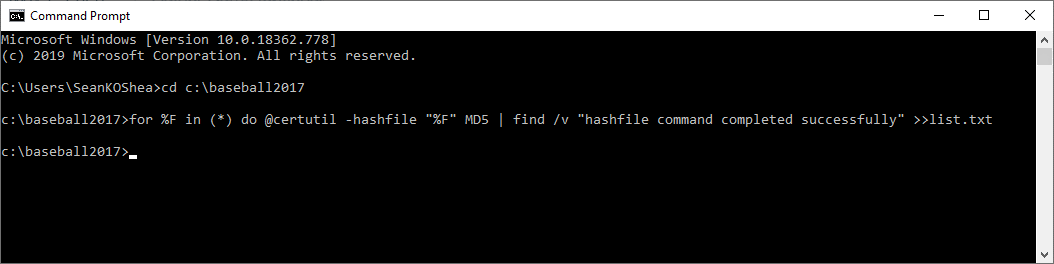
Powershell can compare output using the Compare-Object cmdlet as shown below:Ĭommand: Compare-Object (Get-Content C:\old.csv) (Get-Content C:\new.csv) Format-Table -Wrap | Out-File C:\final.txtĬertutil is another native windows program that you may use to compute Hashes of files and can easily run via either Powershell or Command Prompt.7-Zip is probably the most popular and well known free file archiver around today. Ideally, we would want to compare the hashes when the script is run against the baseline, and report any changes. If we make a change to readme.txt inside nc directory, when we run the command again the output of the hash will be different. csv file then you can use the following command to export the results with -Recurse parameter which will recurse the file system and take the hashes of any files within sub-folders.Ĭommand: Get-ChildItem -Recurse | Get-FileHash | Export-Csv -Path C:\output.csvįor XML, you can use Export-Clixml parameter. In case if you want to generate hash with MD5, the command is:Ĭommand: Get-FileHash C:\filename -Algorithm MD5Īnd if you want to generate a Hash of multiple files, then you can use the following command:Īnd in case, if you want to export all the output in a. The default hashing algorithm is SHA256 but you can use also use MD5, SHA1, SHA384, SHA512, RIPEMD160 and MACTripleDES. To Generate a Hash (SHA256) with Windows Powershell Cmdlets of a single file, the command is: One of the strengths of Windows PowerShell is that cmdlets use a standard naming convention that follows a verb-noun pattern, such as Get-Help, Get-EventLog, or Get-Process. These cmdlets are designed to assist the network administrator or consultant to leverage the power of Windows PowerShell without having to learn a scripting language. The latest version of Windows PowerShell comes with about 1,000 cmdlets on Windows 10, and as additional features and roles are added, so are additional cmdlets. They are not scripts, which are uncompiled code, because they are built using the services of a special. They are like executable programs, but they take advantage of the facilities built into Windows PowerShell, and therefore are easy to write. The Windows PowerShell team creates the core cmdlets, but many other teams at Microsoft were involved in creating the hundreds of cmdlets shipping with Windows 8. In addition to using Windows console applications and built-in commands, you can also use the cmdlets (pronounced commandlets) that are built into Windows PowerShell. Suggested Read: Dump All Wi-Fi Passwords with Windows PowerShell Windows powershell is one of the essential management and automation tool that brings the simplicity of the command line to next generation operating systems. Powershell makes checking the integrity of multiple files very easy by combining Get-ChildItem (or dir/ls)with Get-Filehash. To check the integrity of your system, you can create a baseline of file hashes, and periodically check for changes against the baseline. A hash is always a useful when you need to verify the integrity of any file.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
